
The Geriatric Animal Breeding Facility (GABF) consists of a reproduction and housing unit (breeding facility) and a unit dedicated to research (experimental facility).
It is unique, not only because it is among the very few animal breeding facilities that, nationally and internationally, house small rodents (rats and mice) until aging in an SPF (Specific Pathogen Free) environment, thus guaranteeing a continuous availability of geriatric animals for research activities, but also because the high specialization of the staff in aged animals guarantees their breeding and use in conditions of maximum well-being. Indeed, the entire system - from monitoring to enrichment, from medical interventions to the definition of humanitarian endpoints - was designed to meet the specific needs of an aging living being (see below).
Since 2009 the GABF has ISO 9001 quality certification and follows the FELASA recommendations in the field of good zoo-technical practices and veterinary assistance
|
Rooms with autonomous filtration and air intake system (primary biocontainment)
|
  |
|
Washing and sterilization room: autoclave, class II laminar air flow, automatic washing system for cages and bottles
|
  |
|
Environmental enrichment
|
  |
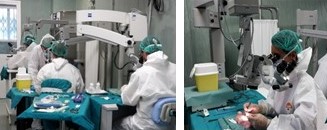
GABF is equipped with a surgical room with operating microscopes, software for data management of animals’ vital para-meters, open or closed-circuit gaseous anesthesia system, medical surgical devices for the practice of experimental micro-surgery. It also offers veterinary advice and assistance (e.g. design and implementation of surgical and pathological models; execution of microsurgical procedures of neurosurgery, abdominal surgery and vascular surgery; anesthetic assi-stance and monitoring of vital parameters during surgery; gavage and intraperitoneal and intravenous administrations; organs explantation and blood sample).
Specifically, the unit dedicated to research includes:
* non-invasive method to permanently identify animals developed in collaboration with Tom Tattoo, Ancona
|
Rodent identification techniques
|
  |
|
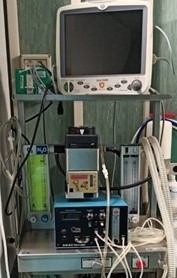
Anesthetic trolley: gaseous anesthesia for rodents with open and closed circuit, monitor for monitoring vital signs, infusion pump, mechanical ventilator for small animals
|
  |
|
Operating microscopes
|
  |
Both standard and genetically modified strains are bred, most of which represent specific models for the study of diseases that predominantly affect geriatric age
 |
|
| Balb/cByJIco | Albino, low prolificacy, adult weight 30 gr, Th2-biased immune system |
| C57BL/6J | Intense black fur, low prolificacy, adult weight 30 gr, genotype with high incidence of mutations |
| FVB/N | Albino, high prolificacy, adult weight 30-35 g, high incidence of spontaneous tumors |
| Samp8 | polyhybrid, albino, premature aging; at 51 weeks it presented cognitive deficits and a lymphoproliferative decline similar to those of elderly mice |
| SAMR1-Ta | Mutant, albino, usually used as control of Samp8 |
| Delta16/Her2 | Transgenic heterozygous for the human oncogene Delta16/Herb-2; females develop early breast tumors between the 12th and the 19th week of age with a high mortality rate, while males occasionally develop single tumors around 8 months of age |
| FVB/neu-NT | Transgenic homozygous for the rat Her-2/neu oncogene; females develop tumors between the 25th and 42nd week of age |
| C57BL6 Twf1-/-: | C57BL/6 background, knockout for the gene that encodes Twf1 protein, used as a model for chronic cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis |
| C57BL6 Twf1+/+: | Control strain for C57BL6 Twf1-/- |
| C57BL6/PDGFR001B6xCre+/- | Heterozygous for the human gene encoding Platelet Derived Growth Factor Receptor (PDGFR), used as a model for systemic sclerosis or scleroderma |
| C57BL6/PDGFR001B6xCre-/- | Control strain for C57BL6 / PDGFR001B6xCre+/- |
| C57BL6/P16-3MR | C57BL/6J background, it has a trimodal fusion protein under the control of the p16Ink4a promoter; contains i) functional fragments of Renilla luciferase, which makes possible to detect senescent cells in vivo; ii) a red fluorescent monomeric protein, which allows to separate senescent cells from tissues by FACS; and iii) the thymidine kinase of the Herpes simplex virus, which allows to selectively eliminate senescent p16-positive cells by administering the prodrug ganciclovir |
| Rattus norvegicus | |
| Wistar | Albino, high prolificacy, adult weight 600-750 g (males) and 500-650 g (females), high incidence of spontaneous tumors |
| Sprague Dawley | Albino, high prolificacy, rapid growth, adult weight 750-800 gr (males) and 600-750 gr (females) |
In line with the Italian law (Decreto Legislativo n. 26 del 4 marzo 2014), the Research Projects (procedures application) and the Scientific Projects (organs and tissues explantation) must follow the specific authorization process that implies the first evaluation by the Animal Walfare Body (OPBA)
|
Veterinarian for Animal Welfare Technician |
Fiorenza Orlando Giovanni Bernardini |
f.orlando@inrca.it g.bernardini@inrca.it |
+39 071 914319 +39 071 914319 |
|||
 |
||||||
| Goal The main goal of the Geriatric Mouse Clinic (GMC) is to promote and accelerate the development of therapies and interventions for age-related diseases in humans through preclinical studies that centralize the aged animals’ welfare to perfectly balance ethical commitments and scientific needs |
||
| The rationale Geroscience is the rationale behind our approach. Geroscience refers to research aimed at investigating the mechanisms of biological aging seeking to i) understand why aging is the major risk factor and driver of common chronic conditions and diseases and ii) use this knowledge to develop preventive/therapeutic protocols useful in the clinical setting. There has been growing recognition that Geroscience approaches can have a much greater impact on health and disease burden than traditional biomedical strategies aimed at treating age-related diseases as singular, non-correlated phenomena |
 |
|
The unique ethical approach The innovative and unique ethical approach that we envision is based on the premise to not induce but, conversely, try to prevent or cure naturally occurring syndromes and pathologies -comparable to those of the elderly population- associated with old age in animals. Our animals are continually assisted and cared, are bred in an highly enriched environment (e.g. shelters, wooden sticks to gnaw, toys, paper nesting material), always have the indispensable social contacts, and are monitored using parameters and scores defined ad hoc for aged mice. Moreover, we provide veterinarian interventions with extremely high percentage of success for treating spontaneous problems that develop during aging (e.g. dermatitis, dental malocclusion, conjunctivitis) |
||
The strategy Thanks to the highly specialized Geriatric Animal Breeding Facility of INRCA that provides animals in old and geriatric age, the GMC continuously develops, optimizes and standardizes non-invasive procedures to apply for the clinical, physical and cognitive/behavioral assessment of old and geriatric mice. The screens in the GMC are optimized in time and non-invasiveness (Table 1) and include clinical reports (clinical frailty index – causes of death), anthropometry data (shrinkness), physical strength measurements (weakness), endurance (fatigue), speed, activity (poor mobility), cognitive frailty (habituation, spatial long-term and working memory, recognition memory, aversive memory), anxiety level, heart monitoring (ECG) as well as survival (longevity) |
||
 |
PI for frailty and longevity studies PI for behavioral/cognitive function studies Veterinary Staff |
Marco Malavolta Marta Balietti Fiorenza Orlando |
m.malavolta@inrca.it m.balietti@inrca.it f.orlando@inrca.it |
||||
Overview of phenotypic procedures and tools available at the Geriatric Mouse Clinic |
|
  |
Clinical ReportParametersClinical frailty index (minimum 31 items)  |
  |
Postmortem ExaminationParametersCauses of death |
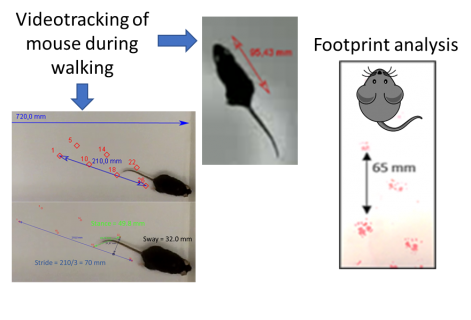  |
Anthropometry data (shrinkness)ParametersBody length during walking (videotracking) and stride length (videotracking and footprint analysis) |
  |
Grip strength (weakness)ParametersStrength scores and peak force |
  |
Treadmill test for measurement of endurance (fatigue)ParametersDistance covered |
  |
Rotarod test for measurements of endurance, balance, speed and motor coordinationParametersLatency and max speed |
 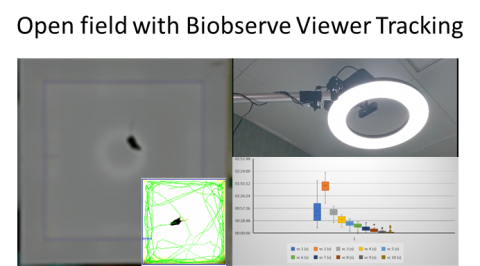 |
Locomotor activity test with Biobserve III Viewer for measurements of activity and speedParametersTrack length, max speed kept for 3s, percent area explored, and many other customizable parameters |
  |
Barnes test for spatial learning and memory (cognitive frailty)ParametersLatency time during training, latency and time spent in target quadrant during the probe day |
  |
Novel object recognition test for analysis of recognition memory, which is part of episodic memoryParametersTime spent exploring the novel object and discrimination index |
  |
Open Field test to analyze habituation, the simplest form of learningParametersDistance moved per each minute of recording |
  |
Elevated Plus Maze test to assay anxiety levelParametersPercent time spent in the open arms of the arena, number of entries in the open arms, and number of head dipping |
 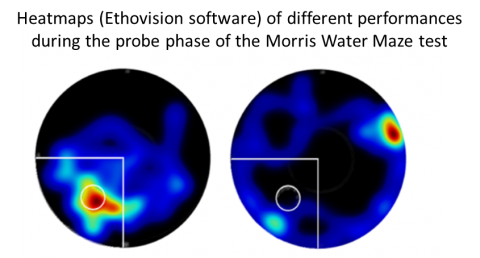 |
Morris Water Maze test to evaluate the spatial long-term memoryParametersPercent time spent in the target quadrant and mean distance from the previous position of the platform |
 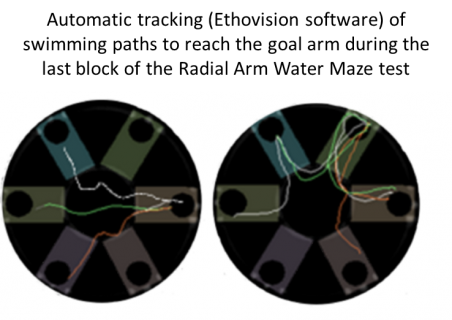 |
Radial Arm Water Maze test to study spatial reference and working memoryParametersNumber of errors in the last block |
  |
Step-Through Passive Avoidance test to define the long-term aversive memoryParametersLatency, i.e. time spent to enter the dark compartment after the conditioning |
 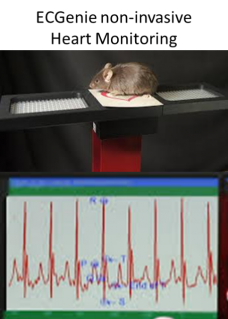 |
ECGenie Heart MonitoringParametersHeart rate, heart rate variability, PSQT interval durations |
 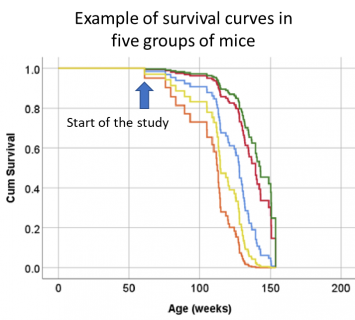 |
Survival (longevity)ParametersMean and max survival (Kaplan Meier and Cox Regression with covariates) |
 IRCCS INRCA
IRCCS INRCA